This tutorial explains in details how to install Git on a Debian 10 Buster instance.
Created in 2005 by Linus Torvalds, Git is by far the most commonly used distributed version control system in the world.
This tool is mainly used by development teams to keep track of all the changes happening on a code base, as well as organizing code in individual branches.
It is for example used by very big companies such as GitHub, Gitlab or Bitbucket.
In today’s tutorial, we are going to see how to setup Git on a Debian 10 Buster machine.
Debian 10 is brand new, so if you need a complete setup tutorial for Debian 10 Buster, follow this tutorial
I – Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure that you have root privileges on your instance.
To make sure of it, run the following command.
$ sudo -l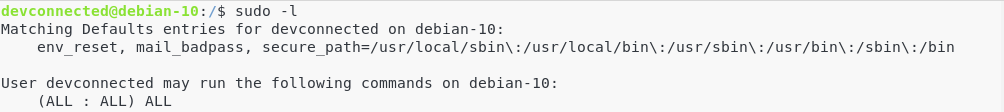
II – Install Git from official sources
a – Update your apt repositories
First of all, make sure that you have the latest versions of the repositories on your apt cache.
To update them, run the following command:
$ sudo apt update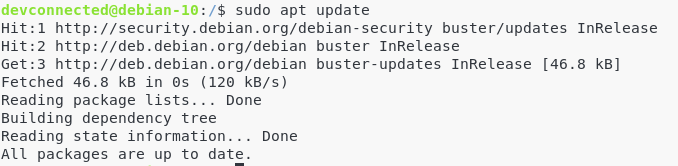
b – Install Git from the official repository
To install the latest stable version of Git (2.20.1 in my case), run the following command.
$ sudo apt-get install git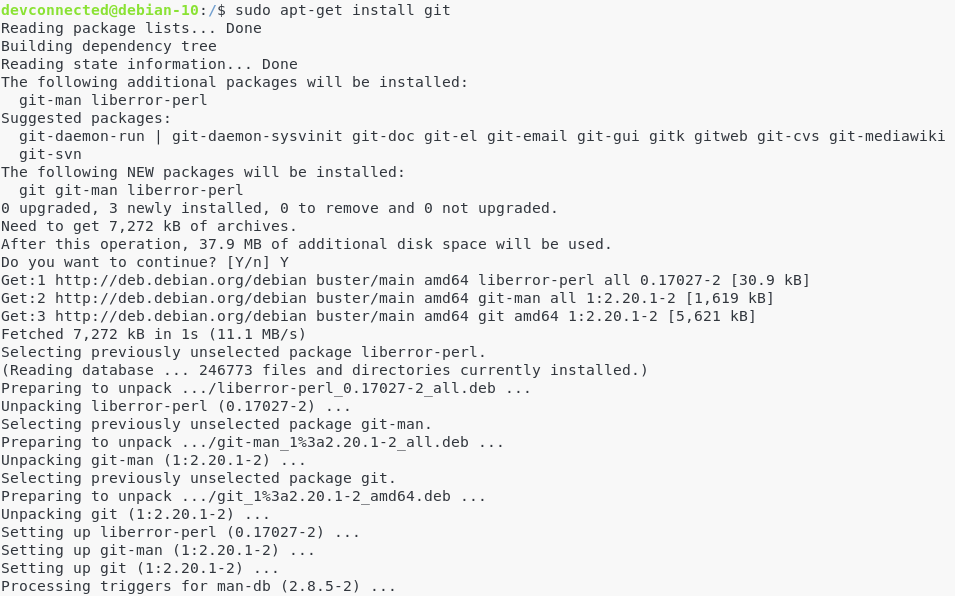
Great!
Now you can check the git version that is running on your computer.
$ git --version
2.20.1III – Installing Git From Source
As you probably noticed, you are not getting the latest version of Git with the apt repositories.
As of August 2019, the latest Git version is 2.22.0.
In order to install the latest Git version on your Debian 10 instance, follow those instructions.
a – Install required dependencies
In order to build Git, you will have to install manually dependencies on your system. To do so, run the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install dh-autoreconf libcurl4-gnutls-dev libexpat1-dev \
gettext libz-dev libssl-dev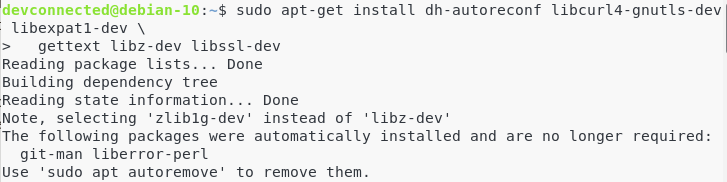
b – Install documentation dependencies
In order to add documentation to Git (in different formats), you will need the following dependencies
$ sudo apt-get install asciidoc xmlto docbook2x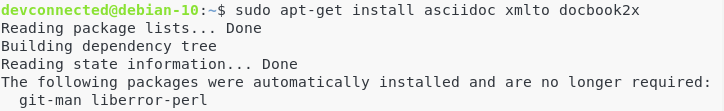
c – Install the install-info dependencies
On Debian configurations, you will need to add the install-info dependency to your system.
$ sudo apt-get install install-info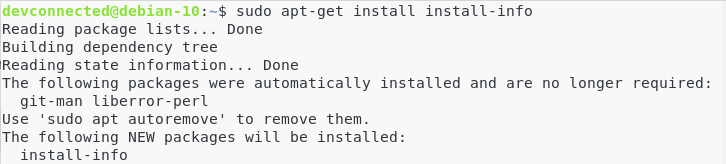
d – Download and build the latest Git version
Head to the Git repository on Github, and select the version you want to run on your Debian instance.
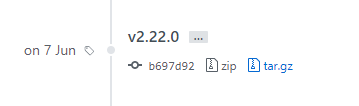
Head to the directory where you stored the tar.gz file, and run the following commands.
$ tar -zxf git-2.22.0.tar.gz
$ cd git-2.22.0
$ make configure
$ ./configure --prefix=/usr
$ make all doc info
$ sudo make install install-doc install-html install-infoAgain, run the following command to make sure that Git is correctly installed on your system
$ git --version
IV – Configuring Git
Now that Git is correctly set on your instance, it is time for you to configure it.
This information is used when you are committing to repositories, you want to make sure that you are appearing under the correct name and email address.
To configure Git, run the following commands:
$ git config --global user.name "devconnected"
$ git config --global user.email "[email protected]"Now to make sure that your changes are made, run the following command.
$ git config --list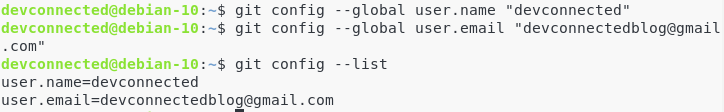
You can also look at your modifications in the gitconfig file available at your home directory.
To view it, run the following command.
$ cat ~/.gitconfig
Now that your Git instance is up and running, it is time for you to make your first contributions to the open source world!
Here’s a very good link by Digital Ocean on a first introduction to the Open Source world!
V – Uninstalling Git
If by any chance you are looking for removing Git from your Debian 10 Buster instance, run the following command:
$ sudo apt-get remove git
Until then, have fun, as always.

