On Linux, hidden files are files that are not directly displayed when performing a standard ls directory listing.
Hidden files, also called dot files on Unix operating systems, are files used in order to execute some scripts or to store configuration about some services on your host.
Some popular example of hidden files are the files contained in the user home directory : .bashrc that stores user initialization scripts or .bash_logout that is executed whenever you leave a bash session.
In some cases, you want to be able to find hidden files easily in order to tweak configuration defaults.
We are going to see all the methods used in order to show hidden files on Linux.
Show Hidden Files on Linux using ls
The easiest way to show hidden files on Linux is to use the ls command with the “-a” option for “all”.
$ ls -a <path>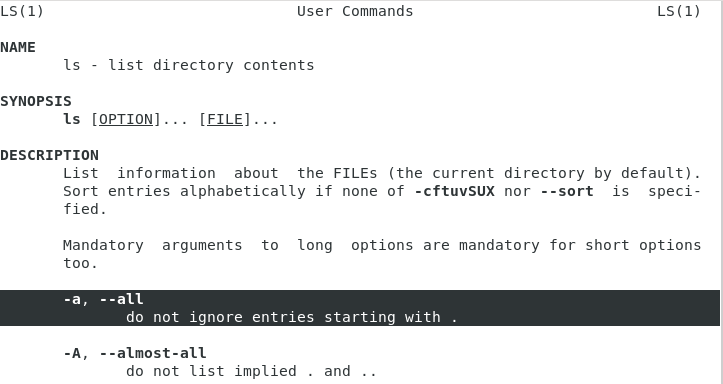
For example, in order to show hidden files in a user home directory, this is the command that you would run.
Alternatively, you can use the “-A” flag in order to show hidden files on Linux.
Using “A”, implied files will not be shown (for example the previous folder also named “.”)
$ ls -al ~
total 356
drwxr-xr-x 14 schkn schkn 4096 Oct 26 06:08 . <-- Not shown with -A
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Jan 5 2019 .. <-- Not shown with -A
-rw------- 1 schkn schkn 43436 Oct 26 06:08 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 220 Apr 4 2018 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 3771 Apr 4 2018 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 schkn schkn 4096 Jan 5 2019 .cache
$ ls -A ~
total 348
-rw------- 1 schkn schkn 43436 Oct 26 06:08 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 220 Apr 4 2018 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 3771 Apr 4 2018 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 schkn schkn 4096 Jan 5 2019 .cacheIn this case, the hidden files are the bash_history, the bash_logout, the bashrc and the cache files.
Show Exclusively Hidden Files using ls
In some cases, you are not interested in other files that the ones that are hidden.
To show exclusively hidden files on Linux, use the ls command with a special regex.
$ ls -dl .[^.]* <path>For example, given the example we have described before, we would get the following output.
$ ls -dl .[^.]* ~
-rw------- 1 schkn schkn 43436 Oct 26 06:08 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 220 Apr 4 2018 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 3771 Apr 4 2018 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 schkn schkn 4096 Jan 5 2019 .cache
drwx------ 5 schkn schkn 4096 Jan 5 2019 .configNote that the previous command also show hidden directories in the path specified.
Show Hidden Files on Linux using find
Another powerful way to find hidden files on your entire system is to use the find command with a globbing character.
To show all the hidden files on your system, run “find” with the name option.
$ find / -name ".*" 2> /dev/nullNote that the output of the command is redirected to /dev/null in order not to be presented with the directories that you can’t access.
In order to show hidden files in the current working directory, run “find” with the maxdepth option.
$ find . -name ".*" -maxdepth 1 2> /dev/nullShow Hidden Directories using find
To show hidden directories in the current working directory, without recursive search, use the “find” command and specify the “d” type.
$ find . -name ".*" -maxdepth 1 -type d 2> /dev/null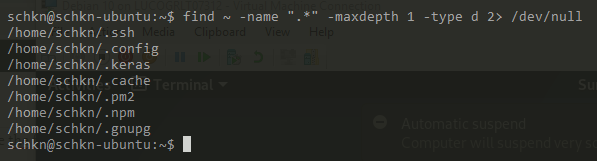
Show Hidden Files on Linux using dir
The dir command is a command close to the ls command on Linux : it displays directory contents on your system.
Similarly to the ls command, it can be used in order to show hidden files in a directory.
To show hidden files, run the “dir” command with the “-a” or the “-A” option (in order to exclude implied files and folders).
$ dir -a <path>
$ dir -A <path>For example, to show hidden files in your home directory, you would run
$ dir -A ~
.bash_history .dbshell .mongorc.js .viminfo scriptsNote that the dir command also show hidden directories that may be located in the path you are search for.
Similarly to the ls command, you can choose to show hidden files exclusively in a folder, not to be bothered with all the other files.
$ dir -dl .[^.]* <path>For example, in the home directory, that would give
$ dir -dl .[^.]* ~
-rw------- 1 schkn schkn 43436 Oct 26 06:08 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 220 Apr 4 2018 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 schkn schkn 3771 Apr 4 2018 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 schkn schkn 4096 Jan 5 2019 .cacheDisplay Hidden Files in GNOME Desktop Environment
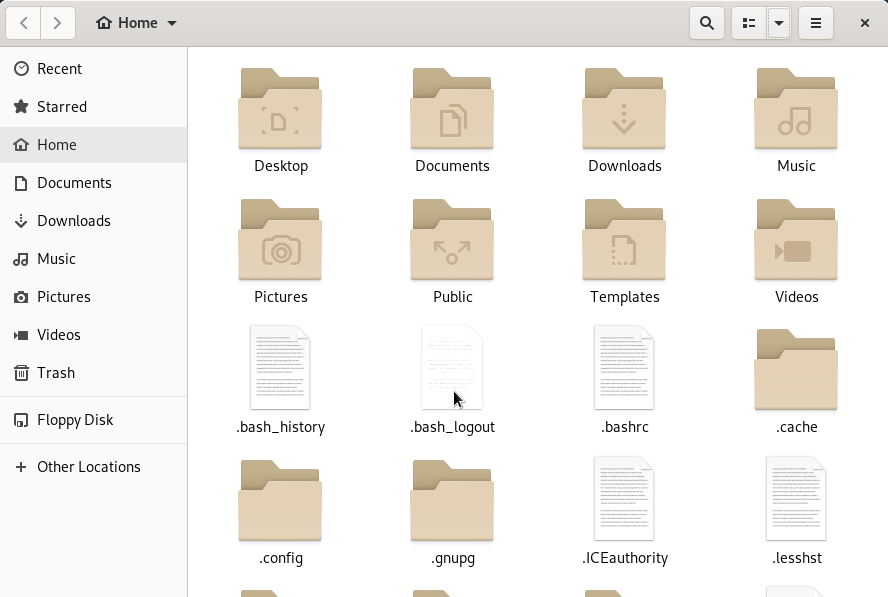
Finally, for those running a GNOME desktop environment, you can also show hidden files when you are browsing your system with a file explorer.
In order to show hidden files via the GNOME interface, click the small bottom arrow located at the top-right corner of the screen.
As a small dropdown appears, make sure to check the “Show Hidden Files” checkbox.
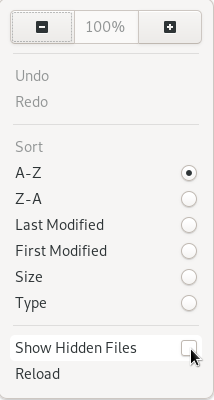
As a consequence, hidden files and folders will be revealed in the File Explorer.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you saw all the ways to show hidden files on Linux : by using the ls command, but you also have the find and the dir command available to you.
If you are using a GNOME desktop environment, there is an option to display them easily with a small option.
If you are interested in Linux System Administration, we have a complete section on the website dedicated to it.



2 comments
[…] How To Show Hidden Files on Linux […]
[…] Hide files and show hidden files […]